The CARP system is designed as a unified "air traffic control" layer for high-volume fulfillment campuses. Its architecture is built upon a microservices, event-driven platform (HLR-08), prioritizing safety (HLR-04), fault tolerance (NFR-010), and real-time performance (NFR-001).
1. CARP Component Breakdown and Responsibilities
The CARP system consists of nine primary, highly cohesive microservices, each identified by a unique, traceable ID (CARP-M for Module). Defining these components first establishes the vocabulary used throughout the design.
CARP-M0: Apache Kafka Event Bus (The Data Backbone)
Central message queue for asynchronous communication, buffering, and real-time data flow between all components. High-priority topics ensure critical commands (like safety stops) are processed instantly (NFR-003).
CARP-M1: Digital Twin Service (Source of Truth)
Maintains the authoritative, live, unified 3D map of the warehouse (HLR-0.1, FR-060). It fuses robot position data (FR-062), tracks dynamic obstacles and human zones, and serves as the global state repository for all planning and safety modules.
CARP-M2: Mission Orchestration Service
Manages the end-to-end lifecycle of a work order. It ingests tasks (FR-001), prioritizes them by SLA (HLR-06), and breaks them into complex, multi-leg missions spanning drone and AMR activity (HLR-02, FR-003) with explicit handoff points.
CARP-M3: Fleet Scheduling Service (MRTA)
The core task allocation engine (HLR-03). It uses a utility scoring function to evaluate the optimal robot or team for a mission leg, considering capability (FR-010), location, State of Charge (SoC), projected mission energy (FR-011), and penalty for unnecessary travel (FR-012). It can safely reassign tasks mid-mission (FR-013).
CARP-M4: Traffic Control & Planning Service
Manages 3D path planning and global deconfliction (HLR-01, HLR-05). It computes time-expanded, collision-free paths (FR-020) for all robots, rapidly replanning routes (NFR-002) when dynamic zones are triggered. It manages the reservation system (time-window tokens) for shared resources like aisle crossings and elevators (FR-022).
CARP-M5: Safety Management Service
The critical safety enforcement module (HLR-04). It consumes real-time human presence data (FR-031), enforces zone-specific robot behaviors (FR-030), and issues preemptive speed caps/hold commands within milliseconds (FR-032). It manages all authenticated supervisor overrides (FR-033), creating an immutable audit log (FR-034, NFR-091).
CARP-M6: Infrastructure Integration Service
The adapter layer for fixed facility assets (HLR-05). It integrates with proprietary APIs/I/O of elevators, conveyors, and automatic doors (FR-050). It handles the complex scheduling handshake with CARP-M4, ensuring tight synchronization and safety interlocks during resource use (FR-052).
CARP-M7: Robot Adapter Layer (Execution Control)
The Southbound layer translating CARP's generic commands into vendor-specific instructions (HLR-08, NFR-030). It publishes raw robot telemetry (pose, battery health) and enforces core safe stop/loiter behaviors that function independently of cloud connectivity (HLR-07, NFR-011). It is designed to be highly extensible (NFR-031).
CARP-M8: API Gateway and Web UI (Northbound Interface)
The system entry point. The API Gateway enforces strong authentication (MFA, mTLS) and authorization (FR-090). The Web UI (FR-070) provides the live map, KPI dashboard (FR-080), alarm feed (FR-072), and supervisor controls.
CARP-M9: Observability & Telemetry Service
Handles analytics, metrics, and maintenance. It calculates real-time KPIs (FR-080, FR-081), monitors asset health (FR-041), and schedules opportunistic charging/maintenance (FR-040, FR-042). It exposes metrics via OpenTelemetry (NFR-040) and manages policy-based alerting.
2. Top-Level Architecture: The Event-Driven Microservices Platform
The CARP system is structured around the defined components, emphasizing scalability (NFR-004), high availability, and rolling updates (NFR-041).
Architectural View
The system architecture is a clear Hub-and-Spoke model. CARP-M0 (Kafka) acts as the central Hub, through which all microservices communicate. External systems connect via CARP-M8 (API Gateway) for input/output and CARP-M7/M6 (Adapters) for low-level control. This model ensures loose coupling and high performance.
Key Architectural Layers
This breakdown shows how the CARP components map to the functional layers of the overall system.
| Layer | Responsibility | Components Involved |
|---|---|---|
| 1. External Integrations | Data ingestion and final command execution. | WMS/ERP, Robots (AMR/Drone), Facility Infrastructure. |
| 2. Northbound Interface | User access, external API exposure, and task intake. | CARP-M8 (API Gateway & Web UI). |
| 3. Core Logic Plane | Real-time decision-making, planning, and safety enforcement. | CARP-M1 (Digital Twin), CARP-M2 (Orchestration), CARP-M3 (Scheduling), CARP-M4 (Planning), CARP-M5 (Safety). |
| 4. Data Backbone | Asynchronous, decoupled, immutable data flow (FR-091). | CARP-M0 (Apache Kafka Event Bus). |
| 5. Southbound Interface | Robot and infrastructure specific protocol translation. | CARP-M7 (Robot Adapter Layer), CARP-M6 (Infrastructure). |
| 6. Persistence | State storage, logging, and metrics retention. | Time-Series DB, Immutable Audit Logs, Map/Config Store (supported by CARP-M9). |
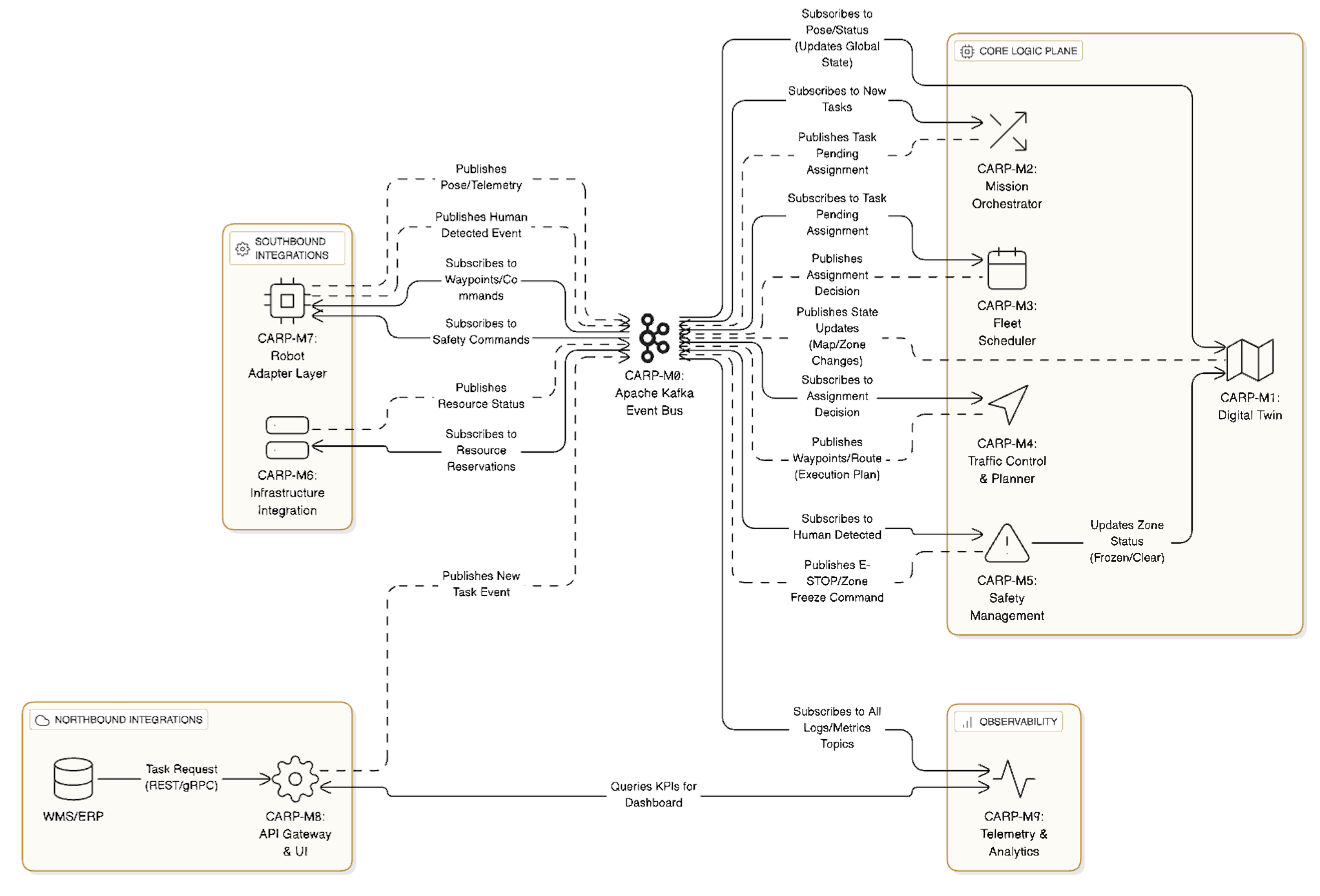 Figure 1. High Level Design UML
Figure 1. High Level Design UML
3. System Execution Flow: CARP in Action
The overall design works as a continuous loop of command, execution, and feedback, centered around the event bus (CARP-M0).
A. Task Lifecycle: From WMS to Robot Command
- Ingestion & Orchestration (CARP-M2): The WMS sends a "Pick Task" request to CARP-M8 (API Gateway). CARP-M2 consumes this event from CARP-M0, validates it (FR-001), and determines it requires a drone to fetch and an AMR for transport (HLR-02). It creates a multi-leg Mission ID.
- Scheduling (CARP-M3): CARP-M2 publishes a "Drone Leg Pending Assignment" event. CARP-M3 consumes this, checks robot status (location, SoC, capability) from the CARP-M1 Digital Twin, and selects the optimal drone (HLR-03). It publishes an "Assignment" event (NFR-001).
- Path Planning (CARP-M4): The Drone Adapter (CARP-M7) and CARP-M4 consume the assignment. CARP-M4 computes a 3D path, reserves the necessary airspace, and schedules the delivery to the handoff point. If a vertical move is needed, it coordinates with CARP-M6 (Infrastructure) to reserve an elevator car (HLR-05).
- Execution (CARP-M7): CARP-M4 streams path waypoints to the drone's specific adapter in CARP-M7, which translates and forwards the commands to the drone. The drone executes the mission, continuously sending pose telemetry back to CARP-M1.
- Completion & Handoff: Once the drone reaches the handoff point, CARP-M2 validates completion (FR-004) and triggers the assignment process for the AMR transport leg.
B. Real-time Safety Intervention
- Detection (External/CARP-M7): A LIDAR sensor detects a human entering Aisle 3 (a defined Stop Zone) and publishes a "Human Presence Detected" event onto CARP-M0 (FR-031).
- Immediate Enforcement (CARP-M5): The Safety Management Service (CARP-M5) consumes this high-priority event. Within milliseconds (NFR-003, FR-032), it identifies the affected robots in that zone (via CARP-M1) and immediately publishes "EMERGENCY STOP" commands to their respective adapters in CARP-M7.
- Execution & Audit (CARP-M7 & M9): The robot adapter (CARP-M7) ensures the drone loiters and the AMR stops (HLR-07). Simultaneously, CARP-M9 logs the incident, and CARP-M5 marks the Aisle 3 zone in the Digital Twin (CARP-M1) as "FROZEN."
- Rerouting (CARP-M4): CARP-M4 receives the "Zone Frozen" update from CARP-M1 and recalculates paths for all approaching robots (NFR-002), diverting traffic until CARP-M5 removes the freeze (HLR-04).
4. Traceability Matrix: HLRs to Design Components
| HLR ID | Requirement Summary | Primary Responsible CARP Component(s) |
|---|---|---|
| HLR-0.1 | Live, unified map of floor and airspace. | CARP-M1 (Digital Twin), CARP-M7 (Adapter Layer), CARP-M8 (Web UI) |
| HLR-02 | Coordinate joint missions (drone fetch/handoff to AMR). | CARP-M2 (Orchestration), CARP-M3 (Scheduling) |
| HLR-03 | Assign tasks based on capability, location, SoC. | CARP-M3 (Scheduling), CARP-M1 (Digital Twin) |
| HLR-04 | Dynamically slow/redirect/hold on human entry; allow human overrides. | CARP-M5 (Safety Management), CARP-M7 (Adapter Layer) |
| HLR-05 | Integrate with shared resources (elevators, conveyors). | CARP-M6 (Infrastructure Integration), CARP-M4 (Traffic Control) |
| HLR-06 | Optimize for order-level SLAs and global flow. | CARP-M3 (Scheduling), CARP-M2 (Orchestration) |
| HLR-07 | Degrade gracefully on comms loss; safe stopping/loiter behaviors. | CARP-M7 (Adapter Layer), CARP-M5 (Safety Management) |
| HLR-08 | Support common fleet/robot APIs and warehouse data systems. | CARP-M8 (API Gateway), CARP-M7 (Adapter Layer) |